
From the user standpoint, email seems so simple. You set the email address of the person to whom you want to send the email, compose your message and click 'Send'.
All done.
In reality, sending your message off into the network cloud is a bit like sending Little Red Riding Hood into the deep dark woods. You never know what might happen.
In this diagram, the sender is a human being using their company account to send an email to someone at a different company.
Step A: Sender creates and sends an email
The originating sender creates an email in their Mail User Agent (MUA) and clicks 'Send'. The MUA is the application the originating sender uses to compose and read email, such as Eudora, Outlook, etc.
Step B: Sender's MDA/MTA routes the email
The sender's MUA transfers the email to a Mail Delivery Agent (MDA). Frequently, the sender's MTA also handles the responsibilities of an MDA. Several of the most common MTAs do this, including sendmail and qmail (which Kavi uses).
The MDA/MTA accepts the email, then routes it to local mailboxes or forwards it if it isn't locally addressed.
In our diagram, an MDA forwards the email to an MTA and it enters the first of a series of "network clouds," labeled as a "Company Network" cloud.
Step C: Network Cloud
An email can encounter a network cloud within a large company or ISP, or the largest network cloud in existence: the Internet. The network cloud may encompass a multitude of mail servers, DNS servers, routers, lions, tigers, bears (wolves!) and other devices and services too numerous to mention. These are prone to be slow when processing an unusually heavy load, temporarily unable to receive an email when taken down for maintenance, and sometimes may not have identified themselves properly to the Internet through the Domain Name System (DNS) so that other MTAs in the network cloud are unable to deliver mail as addressed. These devices may be protected by firewalls, spam filters and malware detection software that may bounce or even delete an email. When an email is deleted by this kind of software, it tends to fail silently, so the sender is given no information about where or when the delivery failure occurred.
Email service providers and other companies that process a large volume of email often have their own, private network clouds. These organizations commonly have multiple mail servers, and route all email through a central gateway server (i.e., mail hub) that redistributes mail to whichever MTA is available. Email on these secondary MTAs must usually wait for the primary MTA (i.e., the designated host for that domain) to become available, at which time the secondary mail server will transfer its messages to the primary MTA.
Step D: Email Queue
The email in the diagram is addressed to someone at another company, so it enters an email queue with other outgoing email messages. If there is a high volume of mail in the queue—either because there are many messages or the messages are unusually large, or both—the message will be delayed in the queue until the MTA processes the messages ahead of it.
Step E: MTA to MTA Transfer
When transferring an email, the sending MTA handles all aspects of mail delivery until the message has been either accepted or rejected by the receiving MTA.
As the email clears the queue, it enters the Internet network cloud, where it is routed along a host-to-host chain of servers. Each MTA in the Internet network cloud needs to "stop and ask directions" from the Domain Name System (DNS) in order to identify the next MTA in the delivery chain. The exact route depends partly on server availability and mostly on which MTA can be found to accept email for the domain specified in the address. Most email takes a path that is dependent on server availability, so a pair of messages originating from the same host and addressed to the same receiving host could take different paths. These days, it's mostly spammers that specify any part of the path, deliberately routing their message through a series of relay servers in an attempt to obscure the true origin of the message.
To find the recipient's IP address and mailbox, the MTA must drill down through the Domain Name System (DNS), which consists of a set of servers distributed across the Internet. Beginning with the root nameservers at the top-level domain (.tld), then domain nameservers that handle requests for domains within that .tld, and eventually to nameservers that know about the local domain.
DNS resolution and transfer process
- There are 13 root servers serving the top-level domains (e.g., .org, .com, .edu, .gov, .net, etc.). These root servers refer requests for a given domain to the root name servers that handle requests for that tld. In practice, this step is seldom necessary.
- The MTA can bypass this step because it has already knows which domain name servers handle requests for these .tlds. It asks the appropriate DNS server which Mail Exchange (MX) servers have knowledge of the subdomain or local host in the email address. The DNS server responds with an MX record: a prioritized list of MX servers for this domain.
- An MX server is really an MTA wearing a different hat, just like a person who holds two jobs with different job titles (or three, if the MTA also handles the responsibilities of an MDA). To the DNS server, the server that accepts messages is an MX server. When is transferring messages, it is called an MTA.
- The MTA contacts the MX servers on the MX record in order of priority until it finds the designated host for that address domain.
- The sending MTA asks if the host accepts messages for the recipient's username at that domain (i.e., username@domain.tld) and transfers the message.
Step F: Firewalls, Spam and Virus Filters
The transfer process described in the last step is somewhat simplified. An email may be transferred to more than one MTA within a network cloud and is likely to be passed to at least one firewall before it reaches it's destination.
An email encountering a firewall may be tested by spam and virus filters before it is allowed to pass inside the firewall. These filters test to see if the message qualifies as spam or malware. If the message contains malware, the file is usually quarantined and the sender is notified. If the message is identified as spam, it will probably be deleted without notifying the sender.
Spam is difficult to detect because it can assume so many different forms, so spam filters test on a broad set of criteria and tend to misclassify a significant number of messages as spam, particularly messages from mailing lists. When an email from a list or other automated source seems to have vanished somewhere in the network cloud, the culprit is usually a spam filter at the receiver's ISP or company. This explained in greater detail in Virus Scanning and Spam Blocking.
Delivery
In the diagram, the email makes it past the hazards of the spam trap...er...filter, and is accepted for delivery by the receiver's MTA. The MTA calls a local MDA to deliver the mail to the correct mailbox, where it will sit until it is retrieved by the recipient's MUA.
RFCs
Documents that define email standards are called "Request For Comments (RFCs)", and are available on the Internet through the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) website. There are many RFCs and they form a somewhat complex, interlocking set of standards, but they are a font of information for anyone interested in gaining a deeper understanding of email.

An increasing number of people of all ages own mobile phones, enjoying the convenience, freedom and re-assurance they provide. There is a range of different handsets and contracts available, providing mobile communication solutions to suit Customers.
Below Points may be Useful to you and if you Follow :
- Fix your budget: Before you do anything else, think about why you want a mobile phone and determine your budget. There are numerous types of call plan, to suit various budgets and needs. There are also services available to help you keep track of what you spend consider whether this would help you and check out what options are available.
- What are your usage patterns: How often will you be using the phone, at what time of day and what will be your average call length? Will you be using the phone mostly for voice calls, or to SMS friends? Your usage patterns may help determine what type of plan is best for you and your budget.
- What types of plan are available: There are four basic types of service agreement: fixed-term contracts, monthly plans, pre-paid or leasing. Pre-paid is ideal if you want to ensure you stay within a specified budget - perfect for teenagers. Getting a pre-paid first is also a good way of finding out what your usage is and helping you decide what type of plan might best suit you. Monthly plans allow you the flexibility of receiving monthly bills without signing a long-term contract. Business users may prefer the convenience of fixed-term, while leasing may suit you if you only need a phone and handset for a short time. New capped' plans (available post or pre-paid, depending on mobile carrier) also offer convenience and value and may suit many users.
- What are the call rates within each plan: Call rates vary from plan-to-plan. It's important to assess both the rates and the call charge calculation methods when assessing your options. Issues to consider include: How are call charges calculated? On some plans you will be billed per second, on others, per block of time used (usually per 30 or 60 seconds), or, on the newer capped' deals (post and pre-paid), call caps' apply to many services, providing value and certainty; Is there a flag fall (an amount paid for each connection, in addition to call costs)? Are there any special offers (eg cheaper calls off-peak, or to friends on the same network, or for SMS)?
- What features do you need in a handset: A basic handset will allow you to make calls and send and receive SMS. You'll need a more sophisticated one if you want to use the phone abroad, use MMS, voice recording, make video calls, download video or access the internet. Other features to consider are battery capacity (some handsets run longer between charges than others), ease of use, and your coverage requirements (see coverage'). Consider what you really need or you'll be paying for features you never use. If you already have a handset, are you eligible for other plans?
- How much flexibility do you need: Consider your need for flexibility - and your budget - before you buy a handset or take out a plan. Are you likely to want the flexibility to upgrade your handset when a new one becomes available? Might you want to change to a different plan in six months? There are many different options for paying for handsets (e.g. up-front, flexi-rent deals, as part of your service agreement), and different plans (whether pre-paid or post-paid) have different terms and conditions for example some include penalties for changing networks, or plans, for example. Read the small print and check you can meet all the minimum conditions of the contract before signing anything.
- What coverage do you require: Where will you be using the phone only in metropolitan areas, or in the country? The two dominant types of mobile network are GSM and CDMA. Check with the carriers where they have coverage to ensure they can provide the service where you need it before signing up. Your coverage requirements may also affect your handset choice (there are CDMA and GSM handsets).
- Evaluate the options: Once you've worked out what you need/want, do your homework; shop around and compare what is available, and what will best suit your likely usage and budget.

MP3 players are pocket-sized electronic devices that have the ability to not only store, but play music and other sound files. Although MP3 players are sophisticated devices and there are many verities, they can be placed into one of three broad categories. These categories include hard drive based players, micro hard drive based players, and flash based players.
Hard drive based MP3 players are typically larger and heavier than their competitors due to the fact that they contain a large capacity hard drive inside. This however, may be one of its only weaknesses. These MP3 players provide the largest capacity, ten gigabytes or more, out of the different types of MP3 players. Due to the fact that ten gigabytes equates to roughly 2,900 MP3 files, most consumers buy these players because they accommodate their entire MP3 collection. However, if you are looking for a player to bring with you on a jog or to use at the gym, you may choose to shy away from these players. Any sudden physical movement may cause the internal mechanical hard drive to skip.
Micro hard drive based MP3 players are similar to their big brothers, the hard drive based players, except that they are a bit smaller, both in physical size and internal storage capacity. These MP3 players hold up to six gigabytes of MP3 files, which equals roughly 1,700 songs. Still boasting a respectable capacity, these players have won over many consumers due to their light-weight, compact size. However, these players are also susceptible to skipping if subjected to intense physical movement. Additionally, both hard drive and micro hard drive based players commonly contain rechargeable batteries that can not be replaced for a new battery, but only recharged. If it's small size and moderate capacity that you are in search of this type of player may be just right.
If neither of these players piques your interest, flash based MP3 players may fit your needs. These ultra compact, low capacity players contain no moving parts and consequently, never skip. Another advantage of these players is that their size and lack of moving parts allow them to use minimal power, causing your batteries to last longer. Also, these players almost always use replaceable, disposable batteries, allowing you to put in a new battery if your player should die in the middle of use. However, flash based MP3 players commonly range in capacity from 32 megabytes (roughly 10 songs) to two gigabytes (roughly 570 songs) at most. Therefore, most consumers with a large music collection tend to shy away from this type of MP3 player while athletes can appreciate the sturdy nature of these devices.
Some of the different types of MP3 players include additional features as well. A few of the hard drive players include a small screen that can display pictures and video that is stored on the internal drive. Other players allow for digital voice recording for future playback.
This Post Says to How to Create or Configure New Dial-up Connections in Windows XP.
Go to Start, then select Control Panel then click Network Connections.
Select Create a New Connection. This brings up the New Connection, which help you to create a new connection.
- Select Connect to the Internet and Click the Next button to continue with the wizard.
- Select Setup my Internet connection manually and Click the Next button.
- Select Connect using a dial-up modem and Click the Next button.
- Type your ISP name in the ISP Name text box. Click Next.
- Enter ISP dial up Phone Number.
- Type your Username and Password.
- Click the Next button to continue.
- Now click Finish to create the icon and finish the setup.
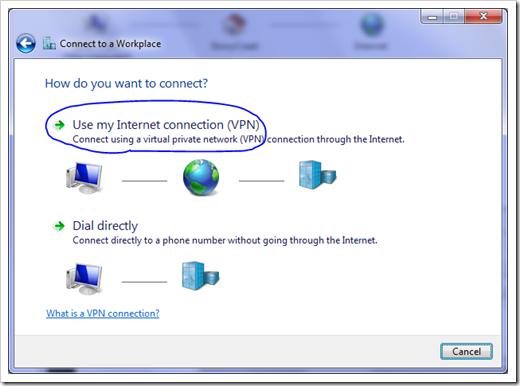
This Below Tutorial will help to Connect Virtual Private Network in Windows Operating System :
- Open the Network Connections option in Control Panel. A list of existing dial-up and LAN connections will appear.
- Choose the 'Create a new connection' option from the left-hand side of the window. First click Next to begin the wizard, then choose the 'Connect to the network at my workplace' item from the list and click Next.
- On the Network Connection page of the wizard, choose the 'Virtual Private Network connection' option and click Next.
- Here type a name for the new VPN connection in the 'Company Name' field and click Next.
- Choose an option on the 'Public Network' screen and click Next. The default option, 'Automatically dial this initial connection' can be used if the VPN connection will always be initiated when the computer is not already connected to the Internet. Otherwise, choose the 'Do not dial the initial connection' option. This option requires that the public Internet connection be established first, before this new VPN connection will be initiated.
- Enter the IP address of the VPN remote access server to connect to, and click Next.
- Choose an option on the "Connection Availability" screen and click Next. The default option, 'My Use Only,' ensures that Windows will make this new connection available only to the currently logged on user. Otherwise, choose the 'Anyone's use' option.
- And the Final Step Click Finish to complete the wizard.

If you want to get some information about any topic using search engine, the search engine will search the given information and will provide a list of links of websites along brief description about each website.
You should use the right search Terms for Relevant results.
The Below Points Must be Noted to Search the Information on the Internet :
- You can type all word in lowercase and also in uppercase, search engine will return the same result. But the best practice is type search keywords always in lowercase.
- Use + sign between words if you want to search the all words. For example, to search Travelling Routes and Maps, then type as: travelling+routes+maps
- To search the exact match, write the words in double quotation marks. For example to search the Movie Theaters, then type as: "Movie Theaters"
- Always avoid to use "and", "or" with search keywords, because these words will affect the search result.

Web Accelerators will Increase Your Browsing Speed
Some Users may be still using any slow dial-up internet connection due to unavailability of any broadband connection in their area. The Web Accelerator application designed to provide the full acceleration for your routine web sites browsing. With the help of Web Accelerator you can browse your internet 4 to 6 times faster than normal dial-up connection. Basically this services compressing the website text data, images and heavy graphics to open or download this data with high speed. This technique is more useful for static websites and for email applications but don't accelerate with secure and downloading audio or video files. Some good web accelerator retains your system cache to reuse websites with faster speed and can also block windows pop-up. If you are using FTP sites and downloading any program using dial-up, then web accelerator is not for you. There are various web accelerator software are free available on Google : Click Here .
Outlook is the Microsoft Office solution for organising and managing e-mail messages, schedules, tasks, notes, contacts and other information. Download Free MS Office Outlook with Serial No.
You can use MS Outlook to manage all your e-mail messages, your calendar and more.
The Ribbon replaces file menu - fully upgraded from 2007 and customisable
The Ribbon gives you faster access to regularly used tools. The ribbon replaces file menus and toolbars of 2003 and compared to 2007, the ribbon can be fully customized. The Ribbon is visible each time you create or edit something in Outlook - such as creating or modifying email messages, calendar items, contacts, tasks or journal entries. It will show tabs and commands that are appropriate for what you are doing.
Backstage View
The Backstage View gives you quick and effective access manage tasks, such as printing, saving, sharing, versioning, protection etc.
Quick Access Toolbar
This is the small toolbar above the Ribbon, and it is there to make the commands you need and use most often, readily available. You can add your favourite commands to it using a right-click.
The Mini Toolbar
Speeds up your access to formatting commands where you need them. For example, in the body of an email message.
New Conversation View
allows you to group your emails from a single message into a single mail item. This streamlines your inbox, and gives you the option to clean up conversations by removing duplicated content. Saving space in your inbox and making it far easier and more efficient to follow a conversation and act on the most recent message.
Quick Steps
This has been improved from 2007 and means you can manage your emails more effectively by allowing you to customise actions for certain emails.
The To-Do Bar to organise tasks and appointments
This is located at the far right of the window and is visible wherever you happen to be working in Outlook. It helps you to keep track of upcoming tasks and appointments.
Using Time Zones for appointments
This function is very useful when you need to create an appointment for a time in another time zone. Once you save the appointment it will be converted to your current time zone set in Outlook.
Instant search
This is a search facility that allows you to search your emails from within your Inbox screen. An enhanced version can be downloaded from Microsoft. Once enabled, you can search multiple fields directly from your Inbox.
Attachment previewing
This is a great new function that speeds up your access to attachments.
New Look to the Calendar
It is easier to use with bigger buttons to switch views, and forward and back buttons, and a new tasks area to track progress. You can overlay calendars to see appointments for two people in the same window.
Calendar and task integration
Using Calendar preview and Multiple Calendar View to simplify scheduling, and managing invitations and responses.
Calendar snapshots
When sending an email, you can now insert a snapshot of your calendar which will appear in the message body showing your availability.
Keyboard shortcuts
Office 2010 makes it easier for you to use shortcuts. Press Alt to see the keyboard shortcuts, you can press the indicated key to show the correct tab and then press the letter to access the command you want.
Outlook 2003 commands in Outlook 2010
You can still use the 2003 commands which makes your transition from one version to another much easier!
People Pane with social networking
A useful function taht allows you to stay connected with colleagues, business and friends with updates using the Outlook Social Connector.
Conversation management
This includes clean up/ignore options which can cut down on duplication of messages and ensure that you respond to the most recent and most relevant emails within a conversation. The 2010 version has improved conversation grouping so it includes messages from all folders, and with the option to include separate accounts.
Group Schedules
2010 gives you the opportunity to group multiple calendars and then view the free and busy times for the entire group of people in one screen.
New graphic and picture-editing tools
To improve the look of your emails.
Manage multiple email accounts from Outlook, such as gmail, or hotmail.
This process has been enhanced in 2010 and has been made a lot easier to use.
Options for sending email
You can make choices about how the message is sent. E.g. whether the email is formatted in Plain text, HTML or Rich Text. You can also change where to store the sent message (or not at all).

India's Best and Top Internet Providers List :
Know more About Communications in India fom Wikipedia.

Get high speed internet access and instant accessibility with DSL (Direct Subscriber Line) technology from airtel broadband.
Click Here to Know more About Airtel Broadband Connection.

Reliance's aim is to provide a never-before internet experience, with this in mind they are constantly reinventing their products with features and services that add value to your life in more ways than one.
Click Here to Know more About Reliance Broadband Connection.

TATA tariff plans are structured keeping your needs in mind. Choose a plan that best fits your requirement. Also enjoy great offers with TATA tariff plans.
Click Here to Know more About Reliance Broadband Connection.
 Idea Broadband Connections in India
Idea Broadband Connections in IndiaIdea is a Product of Aditya Birla Group. IDEA Network Does not Support to Wire Connections and It Works Better on Data Cards and 3G Connections.
Click Here to Know more About Reliance Broadband Connection.

Tikona Digital Networks (TDN) is engaged in building the next generation wireless broadband services for home and enterprise customers in India.
Click Here to Know more About Reliance Broadband Connection.